Drone Understanding UAS Remote Ident guidance has gotten complicated with all the outdated regulations and conflicting advice flying around. Here’s what you actually need to know.
Understanding UAS Remote Identification
Remote identification (RID) technology helps in tracking unmanned aircraft systems (UAS), commonly known as drones. This functionality is crucial for security, safety, and privacy reasons. With the increased popularity of drone usage, regulating and managing airspace has become a pressing need. Various industries, from agriculture to entertainment, utilize UAS. As drone applications expand, ensuring accountable and responsible use becomes essential.

What is UAS Remote Identification?
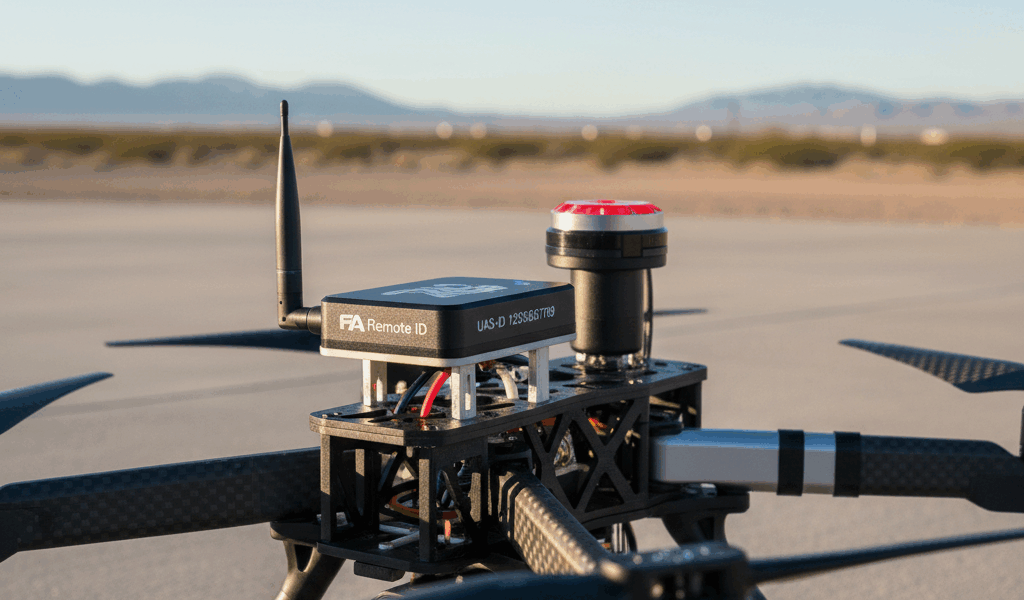
Remote Identification is akin to a digital license plate for drones. It provides vital information about a drone’s activity, location, and operator. This technology aids law enforcement, air traffic management, and the public in identifying drones in their airspace. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) mandates these RID capabilities for most UAS operators in the United States.
Key Components of UAS Remote ID
- Broadcast Module: Transmits real-time data about the drone’s position and identity.
- Network Publishing: Drones can communicate ID information to internet-based services.
- Standard Remote ID: Fully integrated with the drone’s design, allowing seamless operation.
Drones are equipped with either a broadcast module or standard remote ID. The latter is cost-effective and reduces additional hardware requirements. These components ensure data is available to relevant agencies and entities when necessary.
Why Remote ID is Important
Identifying drones in the sky is necessary for ensuring accountability and compliance with aviation regulations. Knowing who operates a drone helps in addressing misuse and privacy invasions. Remote ID can also prevent potential collisions in increasingly crowded airspace. It’s crucial not only for agencies but also for operators to understand and conform to these requirements.
Commercial drone operations benefit significantly from Remote ID. Delivery services and other logistics require precise monitoring. In densely populated urban areas, knowing UAS locations minimizes risks. This technology encourages safer and more efficient integration of UAS into national airspace systems.
Regulatory Requirements
The FAA has laid out clear rules for UAS Remote ID compliance. Operators need to register their drones and ensure they meet the necessary technical standards. The deadline for compliance encourages manufacturers and users to adapt quickly. Understanding these regulations is crucial for anyone involved in drone operations.
Exemptions and Considerations
Not all UAS require Remote ID. Exemptions exist for drones used in education, research, and specific recreational activities. However, owners and operators must stay informed of their responsibilities. Updating knowledge about exemptions can prevent legal complications. Obtaining special waivers can allow flexibility in certain operations where necessary.
Technological Implications
Remote ID technology impacts how drones are designed and built. Manufacturers consider RID integration during the design phase. This requirement encourages innovation in drone technology. Ensuring compatibility with RID systems drives progress in related technologies such as sensors and communication modules. These advances support broader drone applications and capabilities.
Privacy Concerns
With Remote ID, there is tension between operational transparency and privacy. Operators must disclose their identity, but this raises privacy issues. Protecting user data while maintaining transparency is a balance that continues to evolve. Discussions about data use and access are necessary as technology progresses.
Global Perspectives
Remote ID is not just a U.S. policy but a global initiative. Countries are implementing similar strategies to manage UAS. International standards prevent discrepancies and encourage global cooperation. Global policies ensure that UAS operations are harmonious across borders. Such uniformity minimizes complications for multinational drone operators.
While each nation tailors its approach, aligning with international standards allows for cohesive development. Comparing policies from various jurisdictions helps uncover best practices and potential areas for improvement.
Industry Impact
The drone industry feels a significant impact from Remote ID requirements. Manufacturing, retail, and service sectors must adjust their offerings. New opportunities arise in developing compliant hardware and software solutions. Training and education sectors also see growth, providing courses and certifications for operators.
Future Developments
As the landscape changes, future developments in remote ID are likely. Expect advancements in integration, making RID systems more intuitive and efficient. Automation in data management could enhance performance. Resolving current challenges will pave the way for future innovations in unmanned aviation.
The field remains dynamic, fostering ongoing changes that reflect technological, regulatory, and societal trends. Staying informed about these developments is vital for stakeholders in the UAS ecosystem. Engaging in collaborative discussions will shape the future of Remote ID standards and practices.