Drone Understanding UAS in Healthcar guidance has gotten complicated with all the outdated regulations and conflicting advice flying around. Here’s what you actually need to know.
Understanding UAS in Healthcare
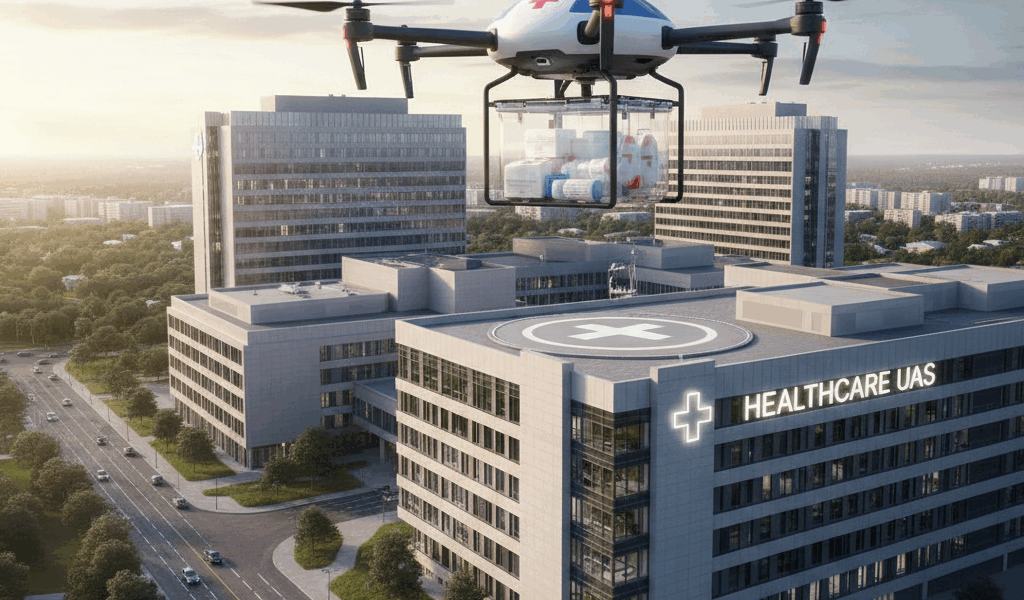
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, emerging technologies continually reshape the way we approach medical treatment and management. Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS), commonly known as drones, are one such innovation demonstrating significant potential in the medical field. These systems are not just transforming logistics but also offering new avenues for delivering care, especially in remote or hard-to-reach regions.

Applications of UAS in the Medical Sector
Drones are being employed in various aspects of healthcare, each offering unique benefits. Their applications range from urgent medical supply deliveries to sophisticated medical examinations. Here’s a breakdown of how UAS are making strides in this critical sector:
- Transport of Medical Supplies: Drones enable swift transportation of medical supplies, including vaccines, medicines, and even blood samples. They’re particularly useful in delivering to remote or inaccessible areas where traditional infrastructure might be lacking.
- Emergency Response: In crisis situations such as natural disasters, drones can be deployed to quickly transport first aid kits, defibrillators, and other emergency supplies to the affected areas, significantly reducing response times.
- Telemedicine Support: In conjunction with telemedicine, UAS can support remote diagnosis and treatment, delivering necessary medications or data devices to patients who cannot travel.
- Medical Imaging: Advancements in drone technology allow for the collection of aerial data and images that can aid in diagnostics, particularly in areas such as agriculture health and environmental monitoring, which indirectly affect human health.
Benefits of Using Drones in Healthcare
Drones offer practical benefits that can revolutionize healthcare delivery. Their use improves not only the efficiency of supply chains but also dramatically enhances patient outcomes. Here are some of the core advantages:
- Speed and Efficiency: Drones bypass ground traffic, which can be crucial during emergencies. Their ability to fly over congested areas means quicker delivery of essential supplies.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Deploying drones can be more economical compared to traditional transport methods, especially in regions with challenging terrain or inadequate infrastructure.
- Expanded Reach: Access to distant and isolated locations becomes viable. Communities cut off by geographical barriers or weather conditions can receive timely medical assistance.
- Data Collection: Beyond delivery, drones can collect environmental and health-related data which can be analyzed for further insights into public health trends and challenges.
- Safety: Drones can safely navigate areas that may be hazardous for humans, such as zones with contagious outbreaks or during conflict situations.
Challenges Faced by UAS in Healthcare
Despite the advantages, implementing drone technology in healthcare isn’t without its hurdles. Several challenges need to be addressed to ensure successful integration into existing systems:
- Regulatory Hurdles: Airspace regulations are stringent for drones, often requiring special permissions and clearances, which can delay deployment. Each country has its regulations which complicates cross-border operations.
- Technical Limitations: Current drones have limitations in battery life and payload capacity. These factors restrict the distance they can travel and the volume of supplies they can carry.
- Privacy Concerns: As drones often use cameras and sensors, they raise significant concerns about patient privacy and data security, necessitating robust regulatory frameworks.
- Weather Dependence: Inclement weather can hinder drone operations. Rain, snow, or high winds can ground drones, limiting their reliability in certain climates.
- Cost of Technology: While operation costs may be low, the initial investment in technology and training can be significant, posing a barrier to widespread adoption.
Case Studies of UAS in Healthcare
Concrete examples of UAS in healthcare have shown promising results worldwide. These case studies highlight the potential impact of drones in medical settings:
Rwanda’s Drone Delivery System
In Rwanda, drones are used to deliver blood and medical supplies to rural clinics. Zipline, a drone delivery service, has partnered with the Rwandan government. Their drones can reach remote areas in minutes instead of hours, showcasing drones’ capability to save lives.
DroneAid in India
As part of the DroneAid initiative, drones were used to deliver COVID-19 vaccines to isolated villages in India. This initiative helped bridge the gap caused by poor road infrastructure, ensuring that vaccines reached those in need promptly.
U.S. Disaster Relief Utilization
During natural disasters in the U.S., emergency services have started employing drones to survey affected areas. This use extends to delivering supplies to trapped or isolated individuals who cannot access immediate help by traditional means.
Future Prospects of Drones in Healthcare
The future looks promising for UAS in healthcare. Technological advancements are set to enhance drone functionality, with improvements in battery life, payload, and autonomous navigation systems. Several companies are investing in research and development to bring these advancements to fruition.
As drones continue to integrate into health systems, they could become central to modern healthcare strategies. Collaboration between policymakers, technologists, and healthcare providers will be crucial to overcome current obstacles and harness the full potential of UAS.
With advances in AI, drones could also potentially assist in diagnostic procedures, gather data for research, and even participate in large-scale health initiatives like vaccination drives. The current trajectory of UAS suggests an even deeper bond between technology and healthcare, paving the way for innovative solutions that could redefine how healthcare is delivered across the globe.